Earthquake: ENEA technology for 'zero damage' buildings and historic centers reconstruction
26/11/2020
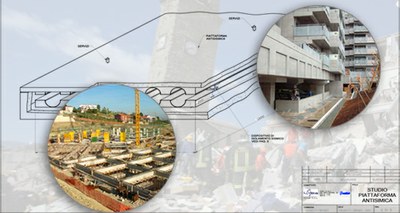 On the occasion of the anniversary of the earthquake of 30 October 2016, the strongest earthquake ever recorded in Italy after that of 1980 in Irpinia, ENEA presents a patent- developed jointly with Tekva, a Tuscan company operating in Italy and abroad in the civil works sector- to build "zero damage" buildings from scratch and to safely rebuild historic centers.
On the occasion of the anniversary of the earthquake of 30 October 2016, the strongest earthquake ever recorded in Italy after that of 1980 in Irpinia, ENEA presents a patent- developed jointly with Tekva, a Tuscan company operating in Italy and abroad in the civil works sector- to build "zero damage" buildings from scratch and to safely rebuild historic centers.
It is a reinforced concrete platform, lightened by fiberglass pipes, which allows to reduce the effects of seismic tremors on buildings by up to 80%, with reduced construction times and competitive costs, respecting the urban and architectural structure of existing urban areas. In addition to seismic isolation, the system offers the possibility of using pipes for the passage of services (water, sewerage, gas, electrical and telephone systems, district heating) making installation, inspection and maintenance simple and economical.
"The system, patented by ENEA and Tekva, offers local technicians and administrators the possibility of reconstructing "as it was" and, where possible, "where it was". This makes it an effective solution for the reconstruction of historic centers in order to preserve their historical value as, for example, in the cases of Amatrice, Accumoli and Arquata del Tronto”, Paolo Clemente, ENEA research manager explained. "On the base, even with a very large surface, it is possible to reproduce pre-existing buildings of any type and material and also complex building aggregates of irregular shape".
At an operational level, after excavation a reinforced concrete base is created, lightened with fiberglass pipes or other materials. Inside the base, between the lower part resting on the ground and the upper part supporting the building, seismic isolation devices are inserted in order to 'decouple' the motion of the building from that of the ground. Perimeter walls connected to the lower parts of the pipes, other walls connected to the upper parts and possible additional dissipation devices complete the work.
“The construction of the base is quick and easy. In general, with seismic isolation more is spent on the foundation but gained in elevation because the overhead structures will be designed and built to withstand very reduced seismic actions and, therefore, with significant savings due to both lower quantity of material and greater simplicity of construction. Seismic isolation is even competitive compared to traditional techniques, at least in areas with medium and high seismicity ", Clemente concluded.
In order to support the reconstruction in the 138 municipalities damaged by the earthquake, in collaboration with CNR-IGAG, INGV and the “G. d'Annunzio "of Chieti-Pescara, ENEA edited the collection of 12 scientific articles dedicated to the estimate of seismic hazard of the territory for a special issue of the Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, entitled "Seismic Microzonation of Central Italy following the 2016-2017 Seismic Sequence ”Issue editors Salomon Hailemikael Sara Amoroso Iolanda Gaudiosi (Vol. 18, Issue 12, Springer- https://link.springer.com/journal/10518/volumes-and-issues/18-12).
The studies were carried out as part of the activities for seismic microzonation of central Italy coordinated by the Center for Seismic Microzonation (CentroMS) and funded by the Government Commissioner for reconstruction, which involved 114 groups of professionals and over 100 researchers including the ENEA experts. The MS Center brings together the major research institutions and university departments with the aim of providing scientific and technical support to those interested in seismic microzonation and its applications, urban planning and geological, geotechnical and geophysical problems related to the seismic emergency.
"The geological-geotechnical characteristics of the sites can contribute to significantly modify the seismic shaking at the foundation and determine other undesirable effects such as landslides, subsidence and ground liquefaction", Salomon Hailemikael at the ENEA Laboratory of Technologies for Structural Dynamics and Seismic and Hydrogeological Risk Prevention explained, that’s why seismic microzonation is crucial to obtain an actual "photograph" of the areas most at risk, useful for safely planning and reconstructing.
ENEA patents and studies are part of the research and technological development activities conducted for the PA, companies and citizens to guarantee support in evaluating policies, plans and strategies for adaptation and mitigation risks deriving from natural and anthropogenic causes, with particular reference to extreme events, such as seismic ones; models and systems for the analysis and development of anthropogenic impact assessment scenarios and reduction of natural risks both locally and nationally for remediation and policy interventions; innovative anti-seismic technologies for civil and industrial buildings and historical-cultural and monumental heritage.
For more information please contact:
Paolo Clemente – ENEA, paolo.clemente@enea.it
