Earthquakes: New technique tested to identify monuments at risk of collapse
19/7/2018
 “Motion magnification”, the technique capable of visually amplifying the vibrations of structures to predict the behavior of buildings in case of earthquake, was tested for the first time in the world on cultural heritage in Italy, at the ENEA Research Center.
“Motion magnification”, the technique capable of visually amplifying the vibrations of structures to predict the behavior of buildings in case of earthquake, was tested for the first time in the world on cultural heritage in Italy, at the ENEA Research Center.
Identify the portions of the most fragile and collapsing monuments or the parts of a fresco more degraded and at risk of detachment, to put them in safety before a seismic shock occurs, is now possible thanks to "motion magnification", an innovative tecnique used by ENEA for the first time in the world on cultural heritage, capable of predicting the behavior of buildings or structures before an earthquake. By amplifying the small movements present in the videos of the vibrations induced by micro natural tremors (wind, traffic, vibrations), this innovation makes the movements of the object analyzed clearly visible, with a detail of a few thousandths of a millimeter.
Developed by the MIT in Boston for applications in the medical and security field, it has been used by ENEA for the monitoring and seismic prevention of cultural heritage, together with the vibrating tables of the ENEA Research Center in central Italy and the 3DVision data acquisition system. The tests are being conducted both on the field-to identify the structural portions at risk of collapse or detachment- and in the laboratory, to experiment with seismic improvement technologies, structural reinforcement of the building heritage and conservation of cultural heritage.
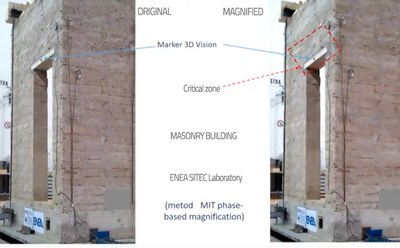 "At ENEA we are capable of combining this technology with the quantitative analysis of frequency values, obtaining a real structural diagnosis of the element analyzed. In practice, the visual analysis of the videos of motion magnification suggests which parts of the building move more markedly when stimulated by weak vibrations generated by traffic, wind, a train and so on ", explained the ENEA researcher Vincenzo Fioriti.
"At ENEA we are capable of combining this technology with the quantitative analysis of frequency values, obtaining a real structural diagnosis of the element analyzed. In practice, the visual analysis of the videos of motion magnification suggests which parts of the building move more markedly when stimulated by weak vibrations generated by traffic, wind, a train and so on ", explained the ENEA researcher Vincenzo Fioriti.
"The degree of amplification depends on the noise present in the digital video to be magnified, that is, the relative motions between the pixels of the films and the number of frames per second", Fioriti continued.
"Thanks to this innovative technology, ENEA is capable of designing preventive measures on the most degraded sections of masonry before an earthquake, and propose a technological and diagnostic offer unique in the world in the projects PON and Horizon 2020, in the areas of prevention and seismic safety ", pointed out the ENEA researcher Gerardo De Canio. "We are in fact capable of monitoring environmental vibrations and dynamically identifying monuments and of conducting 'non-destructive' investigations on structural materials, but also of adopting integrated techniques envisaging a comparison between the magnified motion and the thermographic images and between the results of the sonic tomography and the mechanical tests ".
The field of application of "motion magnification" is quite wide: mechanical fault prevention in engines; monitoring of physiological parameters (e.g. heartbeat); cell analysis; intelligence and security activities through the analysis of facial and vocal expressions. This technology, in fact, allows to reconstruct the sentences pronounced by people on the basis of the movements of the objects located nearby (sheets of paper, containers, glasses) and activated even by speech production.
For more information please contact:
Vincenzo Fioriti, vincenzo.fioriti@enea.it
